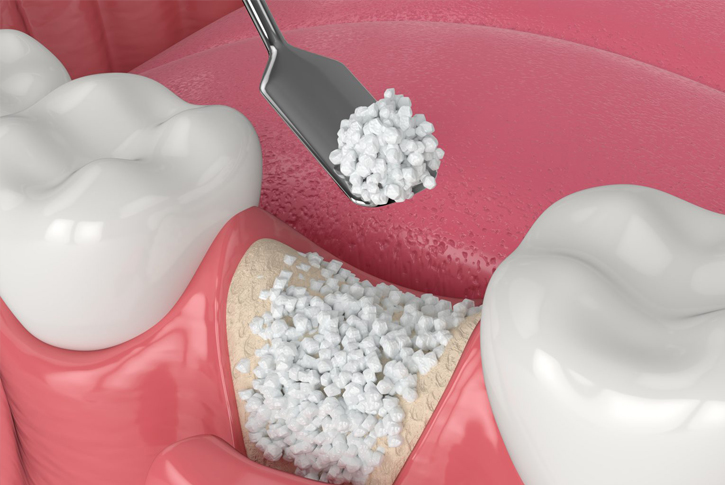
Can you explain bone grafting?
Over time, the jawbone can deteriorate and be absorbed when teeth are missing, leading to insufficient bone for dental implants. This can make many patients ineligible for implant placement.
Fortunately, bone grafting allows us to not only replace missing bone but also stimulate new bone growth. This enables us to place implants of the correct size and shape, restoring both function and appearance.
Different Kinds of Bone Grafts
Autogenous Bone Grafts
Autogenous bone grafts, also referred to as autografts, are created using bone taken from the patient's own body. This bone is typically extracted from areas such as the chin, jaw, lower leg bone, hip, or skull. One of the main advantages of autogenous bone grafts is that the material used is the patient's own live bone, containing living cellular elements that promote bone growth. Additionally, there is no risk of rejection since the bone comes from the patient themselves.
However, a drawback of autografts is that they necessitate a second procedure to harvest bone from another part of the body. Depending on the individual's condition, undergoing a second procedure may not be advisable.
Allogenic Bone
Xenogenic Bone
Xenogenic bone is sourced from non-living bone of a different species, typically a cow, and undergoes high-temperature processing to prevent immune rejection and contamination. Similar to allogenic grafts, xenogenic grafts provide a structure for surrounding bone to grow and fill in the empty space.
Both allogenic and xenogenic bone grafting eliminate the need for a second procedure to harvest your own bone, as seen with autografts. However, since these options do not possess the bone-forming properties of autografts, the process of bone regeneration may be slower and the outcome less predictable.
Alternatives to Bone Grafts
Demineralized Bone Matrix (DBM) or Demineralized Freeze-Dried Bone Allograft (DFDBA)
Graft Composites
- Collagen/ceramic composite that mimics natural bone composition
- DBM combined with bone marrow cells to promote new bone growth
- Collagen/ceramic/autograft composite for bone regeneration
Proteins that promote bone growth and development
Bone morphogenetic proteins (BMPs) are naturally occurring proteins in the body that play a role in promoting and regulating bone formation and healing.
Using synthetic materials for bone grafting eliminates the need for a second procedure to harvest bone, which can reduce risks and pain. Each bone grafting option comes with its own set of risks and benefits. Dr. Khayat will assess your specific needs to determine the most suitable type of bone graft material for you.
